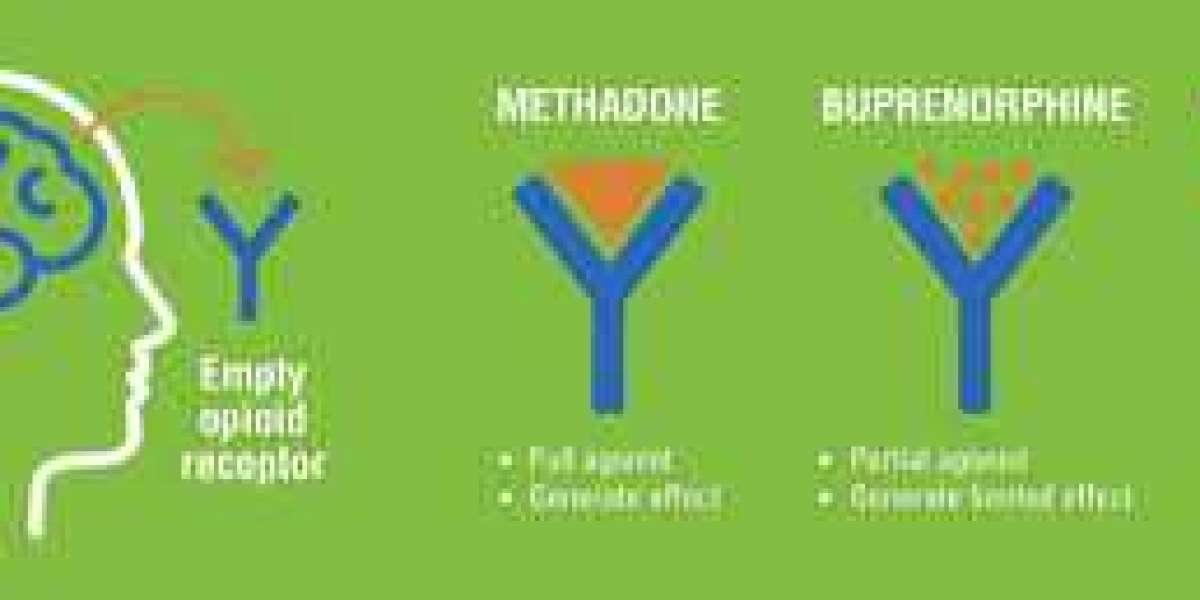
Dopamine, often referred to as the brain’s “reward chemical,” plays a crucial role in regulating mood, motivation, and pleasure. It is a neurotransmitter that acts as a chemical messenger between neurons. While dopamine is vital for healthy brain function, its involvement in the reward system also makes it a key player in addiction.When we engage in pleasurable activities, such as eating, exercising, or socializing, dopamine is released, reinforcing those behaviors. This mechanism is essential for survival and encourages behaviors that promote well-being. However, the same system can become hijacked by addictive substances and behaviors, leading to destructive patterns.Dopamine’s Role in AddictionAddiction is a chronic condition characterized by compulsive substance use or engagement in certain behaviors despite adverse consequences. Substances like drugs and alcohol, as well as activities like gambling, can overstimulate the brain’s reward system, leading to an unnatural surge in dopamine levels.The Dopamine SurgeAddictive substances and behaviors flood the brain with dopamine, creating an intense feeling of euphoria. This spike in dopamine levels far exceeds the natural release triggered by everyday rewards. Over time, the brain begins to associate the substance or behavior with this exaggerated dopamine release, reinforcing the addiction.Dopamine Receptors and ToleranceProlonged exposure to high dopamine levels causes the brain to adapt by reducing the number of dopamine receptors. This process, known as tolerance, means that individuals need larger amounts of the substance or more frequent engagement in the behavior to achieve the same effect, perpetuating the cycle of addiction.Disruption of Natural RewardsAddiction rewires the brain’s reward system, making natural sources of pleasure, such as spending time with loved ones or enjoying hobbies, less rewarding. This shift often isolates individuals and deepens their dependence on the addictive substance or behavior.Dopamine’s Role in RecoveryRecovery from addiction involves reversing the damage caused to the brain’s reward system. While this process can be challenging, it is achievable with the right support and strategies.Restoring Dopamine BalanceRecovery begins with abstinence from the addictive substance or behavior, allowing the brain to gradually restore its natural dopamine levels. This period, often referred to as detox, can be physically and emotionally taxing, as the brain adjusts to functioning without artificial dopamine surges.Rebuilding Natural Reward PathwaysEngaging in healthy activities that promote natural dopamine release is crucial in recovery. Exercise, creative pursuits, and forming meaningful social connections can help rebuild the brain’s reward system and enhance overall well-being.Therapeutic InterventionsBehavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing, are essential components of recovery. These approaches help individuals understand the psychological aspects of addiction, identify triggers, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.Medications and SupportIn some cases, medication-assisted treatment (MAT) may be recommended. These medications can help stabilize dopamine levels and reduce cravings, giving individuals a better chance at long-term recovery.The Social Aspect of RecoverySocial support is a cornerstone of successful addiction recovery. Family, friends, and community resources play a critical role in providing encouragement and accountability. For individuals seeking structured environments, facilities like an old age home in Bandra can offer the support needed to navigate recovery.These homes provide not only medical care but also opportunities for residents to engage in social and recreational activities. By fostering a sense of community and belonging, they help individuals rebuild their lives in a supportive and nurturing environment.Addressing Relapse and ResilienceRelapse is a common part of the recovery journey and should not be viewed as a failure. Instead, it offers an opportunity to identify weaknesses in the recovery plan and make necessary adjustments.Recognizing TriggersStress, negative emotions, and exposure to environments associated with substance use can trigger cravings. Recognizing these triggers and developing strategies to manage them is key to maintaining sobriety.Building ResilienceResilience involves cultivating a mindset that embraces challenges as opportunities for growth. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, journaling, and attending support groups can enhance resilience and provide tools to cope with difficult moments.Long-Term Recovery and Quality of LifeRecovery is not just about abstaining from substances or behaviors but also about restoring a fulfilling and meaningful life. This includes rebuilding relationships, pursuing passions, and maintaining physical and mental health.In urban areas like Bandra, individuals can access various resources to aid in recovery. Whether it’s therapy centers, community groups, or specialized facilities like an old age home in Bandra, these resources provide invaluable support to individuals on their recovery journey. By fostering a sense of stability and belonging, such facilities can significantly enhance the quality of life for those in recovery.ConclusionThe role of dopamine in addiction and recovery highlights the intricate connection between brain chemistry and behavior. While addiction can alter the brain’s reward system, recovery offers the opportunity to heal and rebuild. By addressing the physical, psychological, and social aspects of addiction, individuals can reclaim their lives and achieve lasting well-being.For those seeking a supportive environment during recovery, resources like an old age home in Bandra offer a unique blend of care and community. By integrating medical oversight with social engagement, these facilities provide a solid foundation for individuals to thrive in their recovery journey.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when looking at its layout The point of using Lorem Ipsum.
Contact Us
© 2025 StudentInsta. All rights reserved.
 Meet Ups
Meet Ups
 Experiences
Experiences
 Learning Center
Learning Center
 Accommodation
Accommodation
 Roomie
Roomie
 Ride
Ride
 Spread the Word
Spread the Word
 Student Bazaar
Student Bazaar
 Jobs
Jobs
 Blogs
Blogs
 About StudentInsta
About StudentInsta