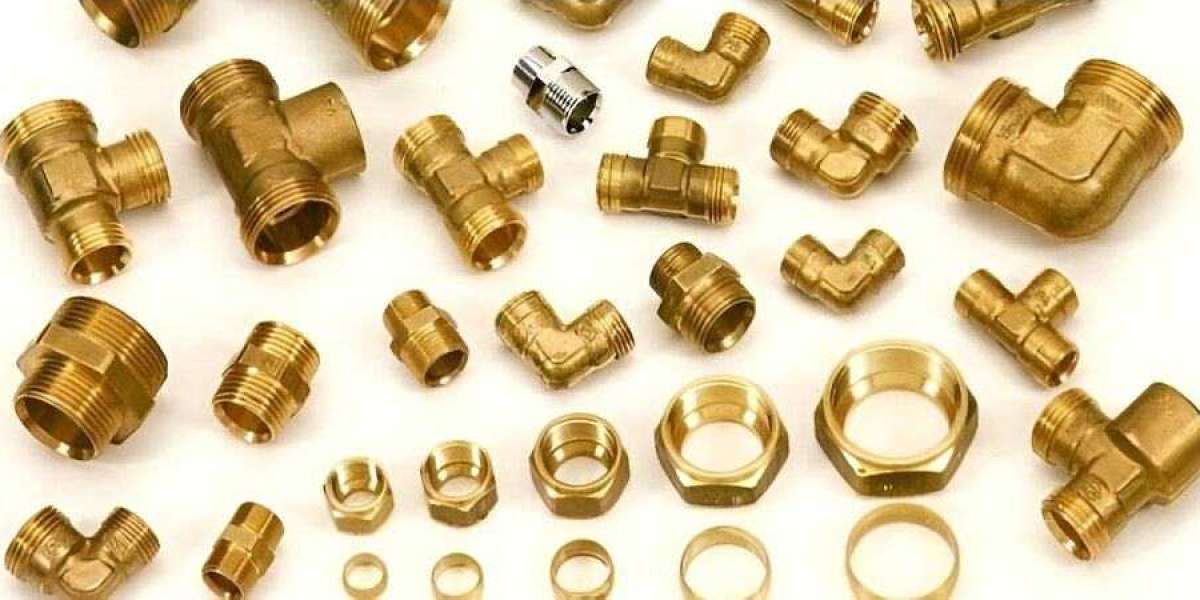
Brass fittings are among the most widely used components in plumbing, gas, and mechanical systems. Known for their durability, corrosion resistance, and versatility, brass fittings play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of piping systems across residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Whether you're a professional plumber, an HVAC technician, or a homeowner tackling a DIY project, understanding the characteristics, types, advantages, and installation of brass pipe fittings is essential. This guide delves deep into everything you need to know about brass pipe fittings—from their composition and benefits to their usage in various environments.
What Is Brass?
Brass is a metal alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, though the exact proportions can vary depending on the intended use. The percentage of copper generally ranges between 55% and 85%, while zinc makes up the balance. In some specialized brass alloys, small amounts of other metals like lead, tin, or iron may be added to enhance certain properties like machinability or strength.
This composition gives brass a unique combination of properties that make it ideal for plumbing and mechanical applications:
High corrosion resistance
Excellent malleability
Thermal conductivity
Aesthetic appeal with a gold-like finish
Low friction coefficient
Brass is also relatively easy to machine and cast, which makes it perfect for the manufacture of precision components like pipe fittings.
Why Choose Brass Pipe Fittings?
Brass fittings are valued for their performance, durability, and reliability. Here are some compelling reasons why brass is a top choice for pipe fittings:
1. Corrosion Resistance
Brass naturally resists corrosion, especially from water, making it a superior choice in plumbing systems where exposure to moisture is inevitable. Unlike iron or steel, brass won’t rust, and it handles soft and hard water effectively without significant degradation.
2. Durability and Longevity
Brass fittings are exceptionally durable and can last for decades without showing signs of wear or failure. They maintain their integrity even under high temperatures and pressures, which makes them suitable for both hot and cold water systems.
3. Versatility
Brass fittings are compatible with a wide range of pipes including copper, PEX, and plastic. They're also suitable for gas, air, water, and steam systems.
4. Excellent Malleability
The malleability of brass makes it easier to shape and manufacture, allowing for tight, leak-proof connections. This is especially useful in intricate plumbing layouts.
5. Temperature Tolerance
Brass fittings are stable under a wide range of temperatures. They can typically withstand temperatures from -40°F to 400°F (-40°C to 204°C), making them ideal for hot water distribution and heat systems.
6. Aesthetic Appeal
With its golden hue, brass is also used in visible plumbing installations where aesthetics matter—such as vintage-styled faucets, exposed piping, or decorative hardware.
Types of Brass Pipe Fittings
Brass pipe fittings come in numerous shapes and sizes to accommodate different piping needs and configurations. Below is a breakdown of the most common types:
1. Elbows
Brass elbows are used to change the direction of flow, usually at 45 or 90 degrees. These are common in both residential and commercial piping systems where bends are required.
2. Tees
Tee fittings allow fluid or gas to be split into two different paths. They have three openings and are commonly used in branch line configurations.
3. Couplings
Couplings connect two pieces of pipe together. They can be used to extend pipe lengths or repair damaged sections.
4. Unions
Unions are similar to couplings but allow for easy disconnection and reconnection of pipes. They’re particularly useful in systems that may need future maintenance.
5. Adapters
Adapters are used to connect pipes of different types or sizes. For instance, they can convert a male thread to a female thread or vice versa.
6. Bushings
Bushings allow a larger fitting to be adapted to a smaller pipe. They help in transitioning from one size of pipe to another.
7. Nipples
These are short pieces of brass pipe with male threads on both ends, used to connect two fittings.
8. Caps and Plugs
Caps are used to close the end of a pipe, while plugs fit into a fitting to block flow. These are essential in temporary or permanent shutoffs.
Thread Types and Sizing
Brass pipe fittings are available with various threading options. The most common include:
NPT (National Pipe Thread): A standard in North America for tapered threads that form a tight seal.
BSP (British Standard Pipe): Common outside North America, used in Europe and Asia.
Compression Fittings: Use a compression ring to seal against the pipe without threading.
Sizing
Brass fittings are typically sized based on the nominal pipe size (NPS). This refers to the inside diameter (ID) of the pipe, not the outside diameter (OD). Understanding the sizing system is crucial to ensure a proper fit, especially when mixing different materials.
Applications of Brass Pipe Fittings
Due to their versatility, brass pipe fittings are found in many different settings. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Plumbing Systems
Brass fittings are a staple in both residential and commercial plumbing. They are used to distribute potable water, drain waste, and ventilate sewer gases.
2. HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, brass fittings help in managing refrigerant lines, water lines, and even gas lines.
3. Gas Distribution
Because of their durability and corrosion resistance, brass is often used in natural gas and propane systems.
4. Marine Applications
Brass's resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it ideal for boat plumbing and marine engine systems.
5. Automotive and Industrial Machinery
Brass fittings are used in fuel lines, brake systems, and lubricating systems for their temperature resilience and durability.
6. Compressed Air Systems
Air compressors and pneumatic tools frequently rely on brass fittings for efficient air distribution.
How to Install Brass Pipe Fittings
Correct installation ensures the longevity and leak-free performance of brass fittings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Choose the Right Fitting
Match the fitting to the pipe size and type (copper, PEX, etc.). Ensure thread compatibility (NPT vs BSP).
Step 2: Clean the Threads
Dirt or debris can compromise the seal. Use a wire brush or cloth to clean the male and female threads.
Step 3: Apply Thread Sealant
Use Teflon tape or pipe thread compound on male threads to ensure a tight seal. Wrap clockwise to match the direction of tightening.
Step 4: Tighten the Fitting
Use appropriate tools like pipe wrenches to tighten the fitting. Avoid over-tightening, which can crack the fitting or damage threads.
Step 5: Pressure Test
After installation, conduct a pressure test to ensure there are no leaks. This step is especially important in gas or high-pressure systems.
Maintenance Tips
Even though brass fittings are low maintenance, here are some tips to ensure their longevity:
Regular Inspections: Check for signs of corrosion, wear, or leaks.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Some chemicals can cause dezincification—a form of corrosion where zinc leaches out.
Proper Storage: Store unused brass fittings in a dry environment to avoid oxidation.
Use Compatible Materials: Avoid mixing brass with incompatible metals (like galvanized steel) to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Dezincification: A Brass-Specific Concern
One unique issue with brass is dezincification, where zinc leaches from the alloy due to aggressive water conditions, leaving behind a porous copper structure. This weakens the fitting and can lead to failure.
To combat this, dezincification-resistant (DZR) brass alloys have been developed. These are commonly used in areas with aggressive or highly acidic water.
If you’re unsure whether dezincification could be a problem, consult your local plumbing codes or water utility provider for water quality reports.
Environmental Considerations
Modern brass fittings are increasingly manufactured with low-lead or lead-free alloys, in compliance with environmental and health standards. This is particularly important in systems that transport drinking water.
Look for certifications such as:
NSF/ANSI 61: Ensures the fitting is safe for potable water.
NSF/ANSI 372: Indicates low-lead content.
UPC and CSA Certifications: Regional standards for plumbing safety and performance.
Cost Considerations
While brass fittings are more expensive than their plastic or galvanized steel counterparts, their durability often offsets the initial investment. You’ll save money in the long run through fewer replacements, lower maintenance costs, and better system performance.
Alternatives to Brass Fittings
Depending on your project, you might consider other types of pipe fittings:
PVC/CPVC: Cheaper, but not suitable for high temperatures or pressures.
PEX Fittings: Easy to install, but generally not as durable.
Stainless Steel: Excellent for corrosive environments but much more expensive.
Copper Fittings: Often used with copper piping but more prone to corrosion compared to brass.
Brass often strikes the best balance between performance, cost, and ease of use.
Conclusion
Brass pipe fittings are a cornerstone of modern plumbing and piping systems. Their unique combination of strength, corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and versatility makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications.
Whether you’re designing a new water distribution system, repairing an HVAC unit, or upgrading your gas line, understanding the types, uses, and benefits of brass fittings will help you make the best decisions for safety and efficiency.
Investing in quality brass fittings and installing them correctly can save you significant time, money, and headaches in the long run. As infrastructure ages and sustainability becomes more important, brass continues to prove its value as a reliable, adaptable, and time-tested material in plumbing and beyond.
 Meet Ups
Meet Ups
 Experiences
Experiences
 Learning Center
Learning Center
 Accommodation
Accommodation
 Roomie
Roomie
 Ride
Ride
 Spread the Word
Spread the Word
 Student Bazaar
Student Bazaar
 Jobs
Jobs
 Blogs
Blogs
 About StudentInsta
About StudentInsta

